Note: Clawdbot was renamed to Moltbot, and is now called OpenClaw (handle: @openclaw, website: openclaw.ai). This guide applies to all versions — the configuration process is the same regardless of what name you know it by. For new users, install via
npm install -g openclaw.
OpenClaw supports the usual suspects (OpenAI, Anthropic), but it also lets you plug in any OpenAI-compatible API as a custom provider. I spent a chunk of time getting this working with a few different providers, and there are some gotchas that aren't obvious from the docs. Here's what I learned.
Why bother with custom providers?
Depends on what you need. Maybe you want cheaper inference for bulk tasks, access to a model that isn't on the main platforms, or a provider that keeps data in a specific region for compliance reasons. Some models are just better at certain things, and being able to route between them gives you more control.
What you'll need
- OpenClaw installed and running (
npm install -g openclaw) - API credentials for your custom provider
- Access to the OpenClaw CLI
- Comfort editing JSON config files
Step 1: Find your OpenClaw config
Your config lives at ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json (legacy: ~/.clawdbot/clawdbot.json — the new path is automatically symlinked). This is where provider and model definitions go.
cat ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json
Step 2: Add the provider
Add your provider to the models.providers section in your OpenClaw config. Here's the structure:
{
"models": {
"mode": "merge",
"providers": {
"your-provider-name": {
"baseUrl": "https://api.yourprovider.com/v1",
"apiKey": "your-api-key-here",
"api": "openai-completions",
"models": [
{
"id": "model-name",
"name": "model-name",
"reasoning": false,
"input": ["text"],
"cost": {
"input": 0.01,
"output": 0.03,
"cacheRead": 0,
"cacheWrite": 0
},
"contextWindow": 32000,
"maxTokens": 32000
}
]
}
}
}
}
A few things to note:
baseUrlis the API endpoint for your providerapimust be"openai-completions"for OpenAI-compatible APIsmodels[].idneeds to match exactly what the provider's API expects in the request bodyreasoningshould betrueif the model supports reasoning modecontextWindowis the max tokens the model can take as inputcostis in USD per 1K tokens (used for tracking, not billing)
Step 3: Allowlist the model
This is the part that trips people up. Defining the provider isn't enough. You also need to add the model to the allowlist in agents.defaults.models, or OpenClaw will reject it.
{
"agents": {
"defaults": {
"models": {
"your-provider-name/model-name": {
"alias": "model-shortcut"
}
}
}
}
}
The key format is provider-name/model-name. This is the fully-qualified identifier OpenClaw uses internally, combining your provider name with the model ID.
Step 4: Apply the config
After editing, apply the changes:
openclaw gateway config.apply --file ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json
The gateway restarts automatically to pick up the new config.
Note: Legacy
clawdbotcommands are aliased toopenclawfor backward compatibility, but new installs should use theopenclawcommand.
Full example: Haimaker integration
Here's a working config with Haimaker and two models:
{
"models": {
"mode": "merge",
"providers": {
"haimaker": {
"baseUrl": "https://api.haimaker.ai/v1",
"apiKey": "YOUR-HAIMAKER-API-KEY",
"api": "openai-completions",
"models": [
{
"id": "minimax/minimax-m2",
"name": "minimax/minimax-m2",
"reasoning": true,
"input": ["text"],
"cost": {
"input": 0.255,
"output": 1.02,
"cacheRead": 0,
"cacheWrite": 0
},
"contextWindow": 204800,
"maxTokens": 204800
},
{
"id": "z-ai/glm-4.6",
"name": "z-ai/glm-4.6",
"reasoning": true,
"input": ["text"],
"cost": {
"input": 0.40,
"output": 1.75,
"cacheRead": 0,
"cacheWrite": 0
},
"contextWindow": 202800,
"maxTokens": 131000
}
]
}
}
},
"agents": {
"defaults": {
"models": {
"haimaker/minimax/minimax-m2": {
"alias": "minimax-m2"
},
"haimaker/z-ai/glm-4.6": {
"alias": "glm-4.6"
}
}
}
}
}
Testing it
Once the config is applied, check that everything works:
Run
/modelsto see if your new models show up in the list.Switch to one of them:
/model minimax-m2Run
/statusto confirm you're on the right model.Send a test message and make sure you get a response back.
Common problems
"model not allowed: provider/model-name"
This is the most common one. It means the model isn't in the agents.defaults.models allowlist. Go back to Step 3. The allowlist key needs to be the fully-qualified name, like haimaker/z-ai/glm-4.6, not just glm-4.6.
Model doesn't show up in /models
Check that you actually added the model to the models.providers[].models[] array. It's easy to add the allowlist entry but forget the model definition (or vice versa).
Wrong model getting called
The id field in your model definition has to match exactly what the provider's API expects. Check their docs. If they expect minimax-m2 but you have minimax/minimax-m2, the request will either fail or hit a different model.
Connection errors
Double-check baseUrl and apiKey. Test the API directly with curl first:
curl https://api.yourprovider.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your-api-key" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "model-name", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hello"}]}'
If that doesn't work, the problem is with your credentials or endpoint, not OpenClaw.
JSON syntax errors
If you get parsing errors or the config doesn't apply, you can simply ask OpenClaw to fix it:
Hey, can you fix the JSON syntax errors in my openclaw config? I keep getting parse errors.
OpenClaw can often identify and fix common JSON issues like missing commas, incorrect quotes, or malformed objects.
How the request routing works
It helps to understand what OpenClaw does under the hood:
- You type
/model minimax-m2 - OpenClaw resolves the alias:
minimax-m2→haimaker/minimax/minimax-m2 - It looks up the provider config for
haimaker - It sends the request to
https://api.haimaker.ai/v1/chat/completions - The request body contains
{ "model": "minimax/minimax-m2", ... }
The fully-qualified name (haimaker/minimax/minimax-m2) is internal to OpenClaw. The API only sees the model id. That's why both the provider definition and the allowlist entry are required: they serve different purposes.
Why Haimaker?
If you're looking for a provider to try this with, Haimaker is a good fit. It's OpenAI-compatible out of the box, has competitive pricing, and with a single API key you get access to a wide variety of models — not just MiniMax M2 and GLM-4.6, but many others you might not find elsewhere. The latency has been solid in my testing.
About premium subscriptions
There have been reports of providers like Anthropic restricting usage of premium subscriptions (like Claude Max) through third-party automation tools. Using those subscriptions through OpenClaw or similar platforms may violate their terms of service and risk your account.
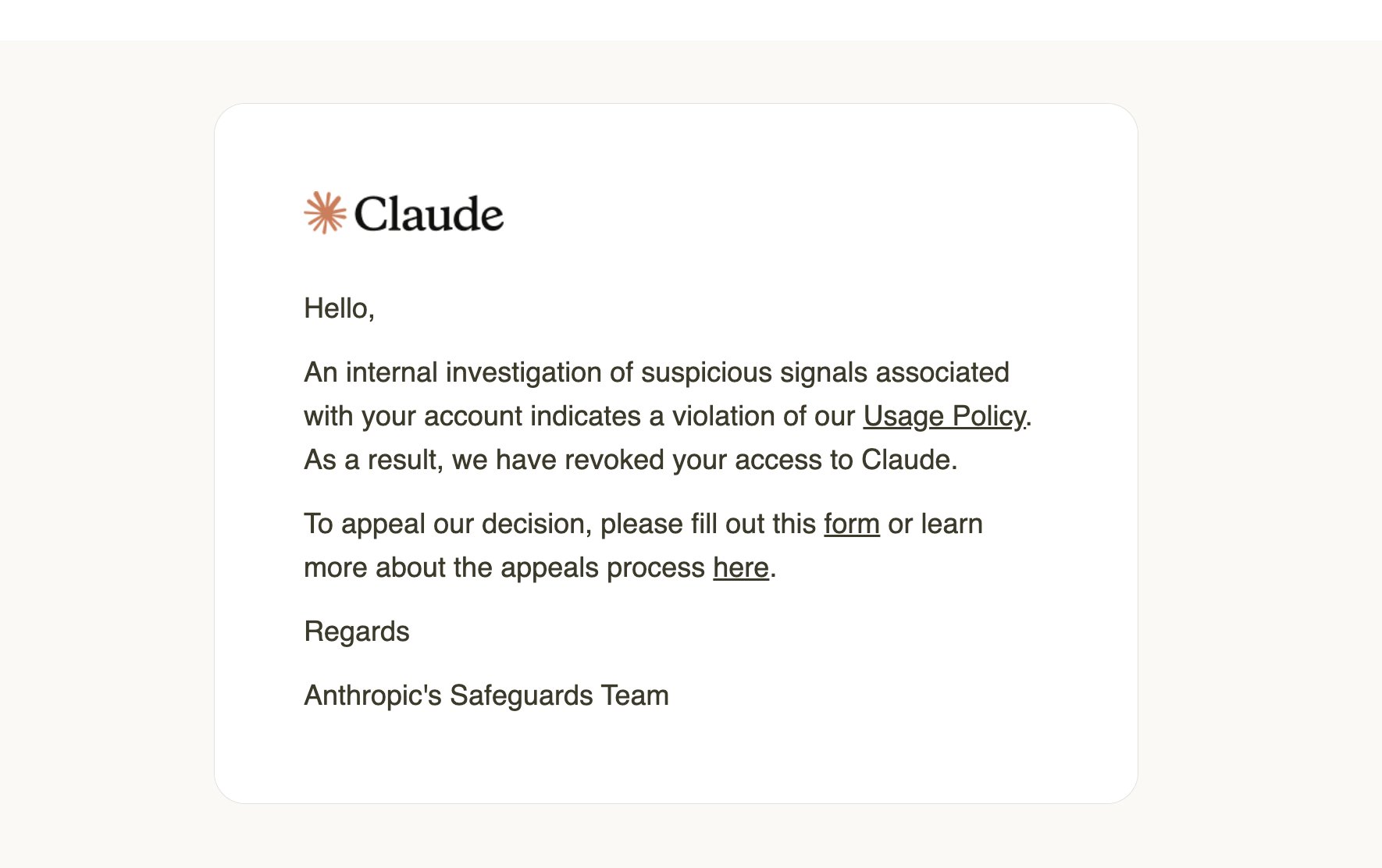
If you're running OpenClaw as an always-on agent, use dedicated API access. It's cheaper in the long run, you won't get banned, and the performance is more consistent for automated workloads.
Get started with Haimaker
Sign up for Haimaker and get $50 in free credits — no subscription lock-in, pay for what you use.
Wrapping up
The whole process comes down to two things: define the provider and its models in models.providers, then add the fully-qualified model names to agents.defaults.models. Miss either step and it won't work.
The allowlist requirement might feel like an extra hoop, but it's there for access control. In multi-agent setups, you probably don't want every agent hitting every model.
If you run into something not covered here, check the OpenClaw documentation or ask in the OpenClaw community Discord.
Written for OpenClaw version 2026.1.30-1. Config structure is backward-compatible with Clawdbot/Moltbot. For the latest updates, visit openclaw.ai.
Related articles:
